Though there are always multiple definitions. Many are general (common and practical in nature). Many are context specific (legal or regulatory for example). The definitions and descriptions we use are general in nature, though they often draw upon more context specific definitions for a more complete meaning.
|
What is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is the production of plants and aquatic life (typically fish) through a system in which the symbiotic relationship between the two is controlled. Simply put, it is a system of growing in which fish provide nutrients for plants to grow and the plants, together with beneficial bacteria, and often composting worms, clean the water for the fish. People provide the care, management, and control.
Aquaponics takes it name from the combination of two popular diciplines: aquaculture and hydroponics.
|
 |
| Aquaponics Operation |
|
|
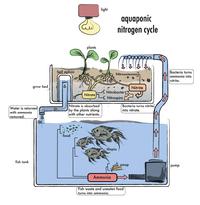 |
| Symbiotic Relationship of Aquaponics |
|
|
Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, shellfish and even plants. The term refers to the cultivation of both marine and freshwater species in systems that can range from land-based, backyard or warehouse systems thru outdoor farming systems, to open-ocean production.
Mariculture is another, more specialized Aquacultural term used to describe the farming of marine organisms in their natural habitats.” The key difference between aquaculture and fencing in wild stock is in cultivation, the proactive effort to improve stock and production.
|
 |
| Aquaculture Operation |
|
|
The definition of Hydroponics can be confusing, and often incorrectly used to describe other systems. We’ll define a hydroponic growing system as one where fertilizer ingredients are in a solution in the root environment of the plants. In our definition, any solid media will be inert, not significantly interacting with the fertilizer or minerals in the water of the system. The plants absorb the nutrients they need from the solution feading their root systems. Soil and other media are not used in a hydroponic system because most usually interact with the water it contains, and effect the nutrient and mineral accessibility.
|
 |
| Hydroponics Operation |
|
|
|